What is Project Budgeting?
Project budgeting is the systematic process of estimating, allocating, and managing financial resources throughout a project’s lifecycle. It’s more than just creating a spreadsheet of numbers—it’s developing a financial roadmap that guides decision-making and ensures project sustainability. Think of it as your project’s financial compass, helping you navigate from initiation to completion while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
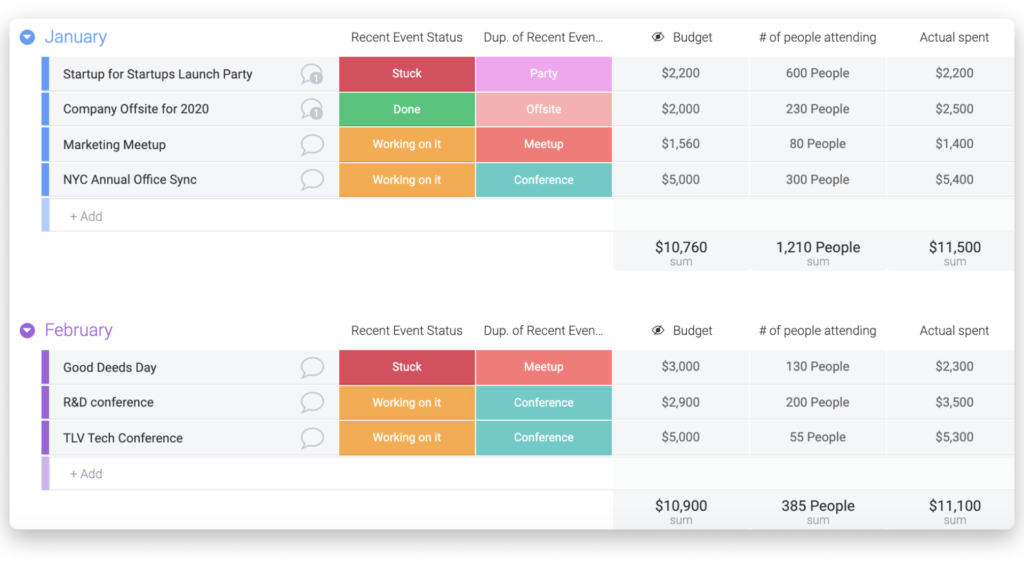
The Four Pillars of Project Budgeting
Successful project budgeting rests on four fundamental components:
Cost Estimation
This involves breaking down your project into discrete tasks and activities, then calculating the expected costs for each component. This includes direct costs like labor and materials, as well as indirect costs such as overhead and administrative expenses.
Budget Allocation
Once costs are estimated, funds need to be strategically distributed across different project areas. This distribution should align with project priorities and timeline requirements while maintaining adequate reserves for contingencies.
Monitoring and Control
Regular tracking of actual spending against planned expenditures is crucial. This ongoing process helps identify variances early and enables timely corrective actions to keep the project financially on track.
Contingency Planning
Given that projects rarely go exactly as planned (Oxford University research shows an average 27% budget overrun), setting aside funds for unexpected expenses is essential. This financial buffer can mean the difference between project success and failure.
Creating an Effective Project Budget
Developing a comprehensive project budget involves several key steps:
Initial Planning
Begin by gathering historical data from similar projects and consulting industry benchmarks. This information provides a realistic foundation for your estimates.
Detailed Breakdown
List all potential cost categories, including:
- Direct labor costs
- Materials and equipment
- External services and contractors
- Overhead expenses
- Training and documentation
- Quality assurance activities
- Risk management reserves
Resource Allocation
Assign specific amounts to each budget category based on:
- Project scope and requirements
- Timeline considerations
- Resource availability
- Market conditions
- Historical performance data
Budget Monitoring and Control
Implementing effective budget control mechanisms is crucial for project success:
Regular Review Cycles
Establish periodic budget reviews to compare actual spending against planned expenditures. These reviews should be frequent enough to catch issues early but not so frequent that they become administratively burdensome.
Variance Analysis
When differences between planned and actual costs occur, conduct thorough analyses to understand:
- Root causes of variances
- Impact on overall project budget
- Potential corrective actions
- Lessons learned for future planning
Performance Metrics
Track key financial indicators such as:
- Cost Performance Index (CPI)
- Budget Variance
- Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- Return on Investment (ROI)
Best Practices for Project Budgeting
To maximize the effectiveness of your project budget:
- Use Appropriate Tools: While spreadsheets might suffice for simple projects, complex initiatives benefit from dedicated project management tools that offer real-time budget tracking and reporting capabilities.
- Build in Flexibility: Allow for some degree of budget adjustment without compromising project objectives. This flexibility can help accommodate minor changes without requiring complete budget revisions.
- Document Assumptions: Clearly record all assumptions made during the budgeting process. This documentation proves invaluable when analyzing variances or adjusting budgets.
- Maintain Clear Communication: Keep stakeholders informed about budget status and any significant changes. Regular financial updates help maintain trust and support for the project.
Avoiding Common Budgeting Pitfalls
Learn from common mistakes to improve your budgeting process:
- Underestimating Costs: Always validate estimates against historical data and expert opinions.
- Ignoring Hidden Costs: Consider all potential expenses, including indirect costs and long-term maintenance requirements.
- Inadequate Monitoring: Implement robust tracking systems to catch issues before they become major problems.
- Poor Risk Management: Allocate sufficient contingency funds based on thorough risk assessment.
By implementing these strategies and maintaining vigilant oversight of your project budget, you can significantly improve your chances of delivering projects within financial constraints. Remember, effective project budgeting isn’t just about controlling costs—it’s about maximizing value and ensuring sustainable project success.


