Understanding Work Breakdown Structure
A Work Breakdown Structure is more than just a task list – it’s a hierarchical decomposition of the total project scope into smaller, more manageable components. Think of it as creating a detailed map of your project, where each path leads to a specific deliverable, and every step is clearly defined. This systematic approach ensures that no critical element is overlooked in the project planning process.
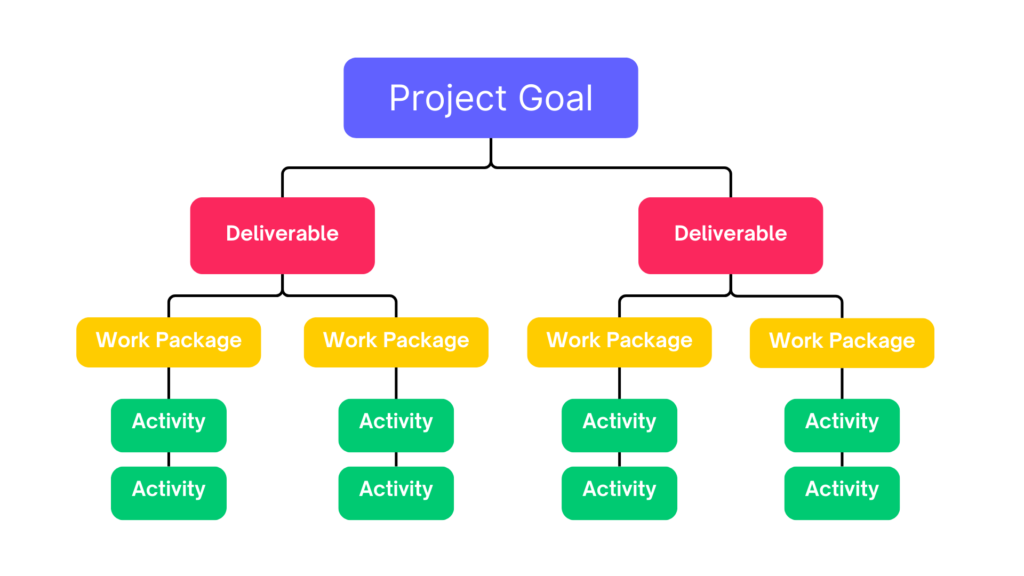
The Fundamental Principle
The core principle behind WBS is the concept of progressive elaboration. Starting with the end goal, each level breaks down into more detailed components until you reach a level of detail that can be effectively managed, scheduled, and monitored. This is often referred to as the “100% rule” – the WBS must capture 100% of the project scope, no more and no less.
Components of a Work Breakdown Structure
Level 1: Project Goal
At the top of the WBS sits the project goal – the ultimate deliverable or outcome. This represents the complete scope of the project and serves as the starting point for breaking down the work.
Level 2: Major Deliverables
The second level identifies the major deliverables or phases required to achieve the project goal. These are the primary building blocks of your project, each representing a significant milestone in the project’s completion.
Level 3: Work Packages
Work packages break down the deliverables into smaller, manageable units. These packages should be:
- Small enough to estimate accurately
- Large enough to maintain meaningful control
- Assignable to a specific individual or team
- Independent of other work packages where possible
Level 4: Activities
The lowest level consists of specific activities or tasks that need to be completed to fulfill each work package. These should be concrete, measurable actions that can be assigned, scheduled, and tracked.
Creating an Effective WBS
Planning Process
Creating an effective WBS begins with understanding the project scope. Follow these steps for successful WBS development:
- Start with the End in Mind Begin by clearly defining the project’s final deliverable. This becomes your Level 1 element and guides all subsequent breakdown decisions.
- Identify Major Components Break down the project into its major components or phases. These should represent significant project milestones or deliverables.
- Decompose Further Continue breaking down each component until you reach a level where tasks are:
- Clearly defined
- Manageable in size
- Easy to estimate
- Simple to monitor
- Review and Refine Examine your WBS to ensure it follows these key principles:
- Mutually exclusive elements (no overlap)
- Collectively exhaustive coverage
- Outcome-oriented decomposition
- Clear and unambiguous naming
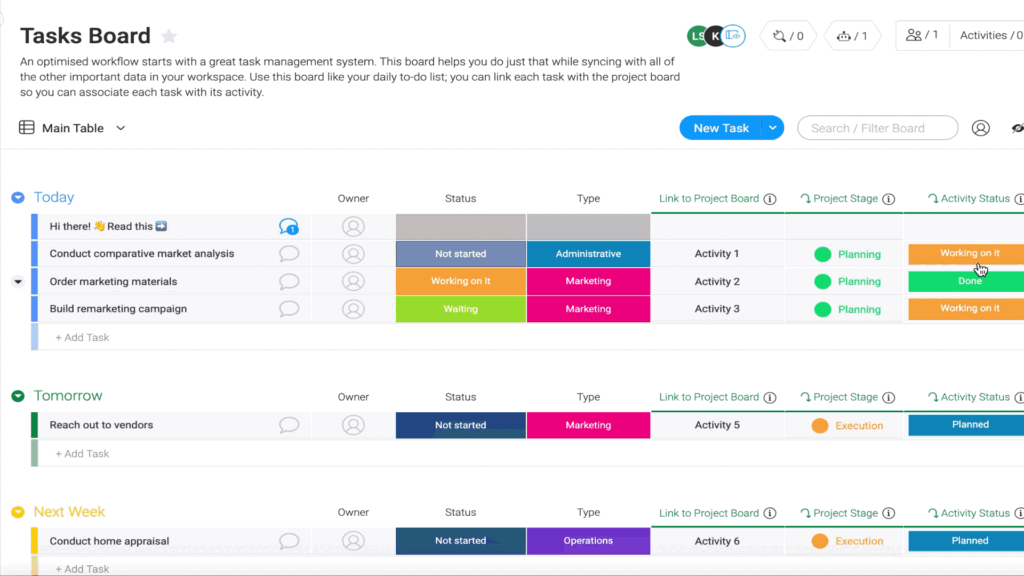
Benefits of Using a Work Breakdown Structure
Enhanced Project Clarity
A well-constructed WBS provides crystal-clear visibility into project scope and requirements. This clarity helps team members understand their roles and responsibilities while giving stakeholders a comprehensive view of project components.
Improved Resource Management
By breaking down the project into detailed components, project managers can more accurately:
- Estimate resource requirements
- Allocate team members effectively
- Plan for equipment and materials needs
- Schedule work in a logical sequence
Better Risk Management
The detailed breakdown helps identify potential risks and challenges early in the project lifecycle. This allows for:
- Proactive risk mitigation
- More accurate contingency planning
- Better understanding of dependencies
- Early identification of potential bottlenecks
More Accurate Estimations
With work broken down into smaller, manageable pieces, estimating becomes more reliable. Teams can:
- Provide more accurate time estimates
- Calculate costs with greater precision
- Plan resources more effectively
- Set realistic deadlines
Practical Application in Project Management Tools
Digital Implementation
Modern project management platforms enable dynamic WBS creation and management. Key features include:
- Visual hierarchy representation
- Drag-and-drop functionality
- Automatic task dependencies
- Progress tracking and reporting
- Resource allocation tools
Integration with Other Project Elements
A WBS serves as the foundation for other project management elements:
- Project schedule development
- Cost estimation and budgeting
- Resource allocation planning
- Risk management strategies
- Quality control measures
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Determining the Right Level of Detail
Solution: Use the “80-hour rule” – break down work packages until they represent no more than 80 hours of work or can be completed within a single reporting period.
Challenge: Maintaining Scope Boundaries
Solution: Regularly review the WBS against the project scope statement to ensure alignment and prevent scope creep.
Challenge: Managing Dependencies
Solution: Create a clear system for identifying and tracking dependencies between work packages and deliverables.
Best Practices for WBS Success
Keep it Deliverable-Oriented
Focus on outcomes rather than actions. Each element should represent a tangible deliverable or result.
Maintain Consistency
Use consistent naming conventions and structuring principles throughout the WBS to ensure clarity and understanding.
Involve the Team
Engage team members in the WBS creation process to benefit from their expertise and ensure buy-in.
Conclusion
A Work Breakdown Structure is more than just a project management tool – it’s a fundamental approach to understanding and controlling project scope. By breaking down complex projects into manageable components, teams can better plan, execute, and monitor their work, leading to more successful project outcomes.
If you need more help, feel free to contact our team.


